Analysis of data obtained over the past two weeks by NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) investigation team shows the spacecraft’s kinetic impact with its target asteroid, Dimorphos, successfully altered the asteroid’s orbit.
This marks humanity’s first time purposely changing the motion of a celestial object and the first full-scale demonstration of asteroid deflection technology.
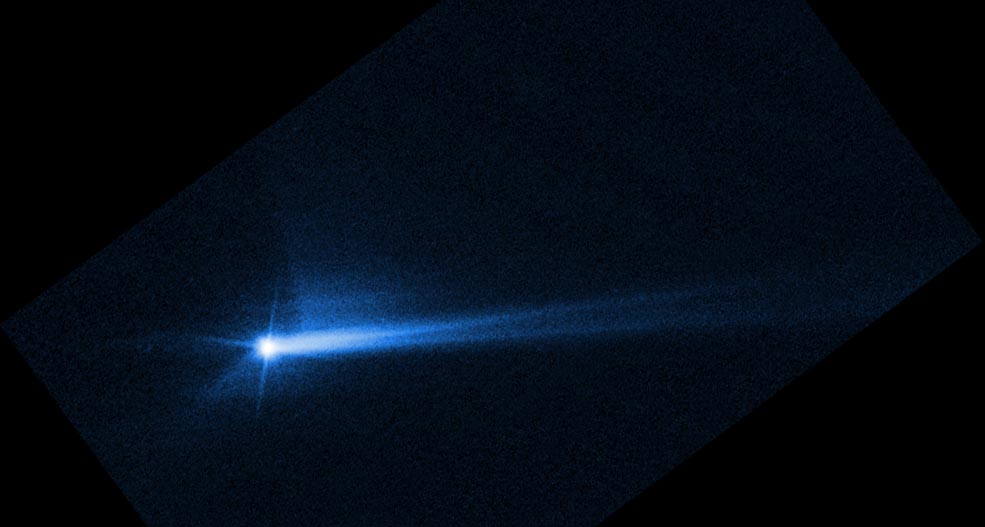
Prior to DART’s impact, it took Dimorphos 11 hours and 55 minutes to orbit its larger parent asteroid, Didymos. Since DART’s intentional collision with Dimorphos on Sept. 26, astronomers have been using telescopes on Earth to measure how much that time has changed. Now, the investigation team has confirmed the spacecraft’s impact altered Dimorphos’ orbit around Didymos by 32 minutes, shortening the 11 hour and 55-minute orbit to 11 hours and 23 minutes. This measurement has a margin of uncertainty of approximately plus or minus 2 minutes.
Focus now is shifting toward measuring the efficiency of momentum transfer from DART’s roughly 14,000-mile (22,530-kilometer) per hour collision with its target. This includes further analysis of the “ejecta” – the many tons of asteroidal rock displaced and launched into space by the impact. The recoil from this blast of debris substantially enhanced DART’s push against Dimorphos – a little like a jet of air streaming out of a balloon sends the balloon in the opposite direction.
To successfully understand the effect of the recoil from the ejecta, more information on of the asteroid’s physical properties, such as the characteristics of its surface, and how strong or weak it is, is needed. These issues are still being investigated.